Filter Your Search 

✖
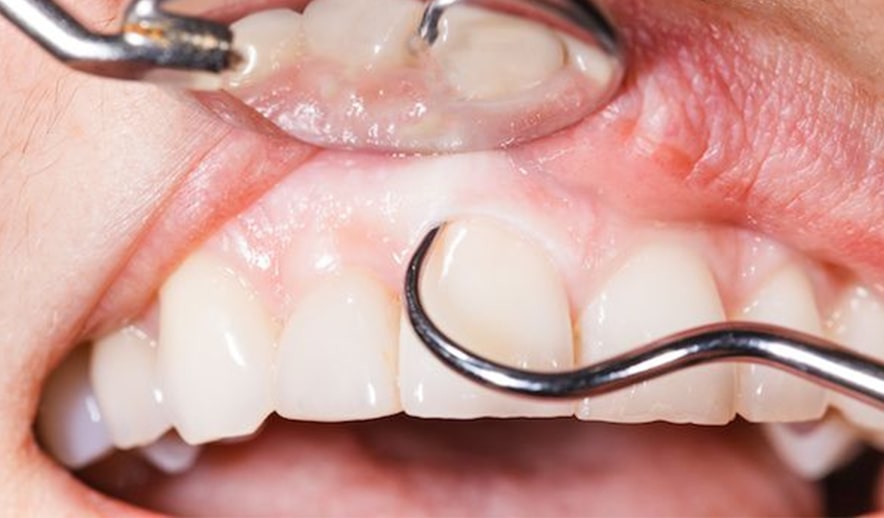
Gum Disease
Gingivitis is a form of periodontal disease. It is inflammation and infection that destroys the tissues that support the teeth, including the gums, the periodontal ligaments and the tooth socket.
Gingivitis is due to long-term effects of plaque deposits on your teeth. Plaque is a sticky material of bacteria, mucus, and food debris that develops on the exposed parts of the teeth. It is a major cause of tooth decay.
If you do not remove the plaque, it turns into a hard deposit called tartar (or calculus) that becomes trapped at the base of the tooth. Plaque and tartar irritate and inflame the gums. Bacteria and the toxins they produce cause the gums to become infected, swollen and tender
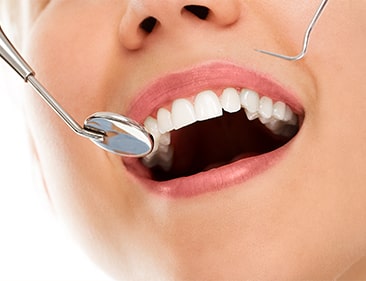
Risk factor for gingivitis
- Poor oral hygiene
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Pregnancy (hormonal changes increase the sensitivity of the gums)
- Misaligned teeth, rough edges of fillings, and ill-fitting or unclean mouth appliances (such as braces, dentures, bridges and crowns)
- Use of certain medications, including phenytoin, bismuth, and some birth control pills
- Many people have some amount of gingivitis. It usually develops during puberty or early adulthood due to hormonal changes. It may persist or recur frequently, depending on the health of your teeth and gums.

Symptoms
- Bleeding gums (blood on toothbrush even with gentle brushing of the teeth)
- Mouth sores
- Red, swollen or tender gums
- Gums that have pulled away from the teeth
- Bad breath that doesn’t go away
- Pus between teeth and gums
- Loose teeth

Treatments
- Initial scale and clean
- Deep cleans (advised by clinician)
- Low-dose oral or topical antibiotics
- Maintenance is done by getting regular check up and cleans every 3-6 monthly